Forget about those pesky cables
 With the speed and security of wired technology, the wireless USB, or the WUSB, is the new trend of wireless devices. Just as Wi-Fi is replacing the Ethernet cable, the wireless USB will most likely replace the regular, wired USB technology. Very soon, devices like hard drives, flash drives, game controllers, digital cameras, printers, scanners, MP3 players or mobile phones will have integrated WUSB technology. Announced in May 2005, the wireless USB, using the Ultra Wide Band, or UWB, a wide spectrum frequency band that operates in the 3.1 to 10.6 GHz and allows the transmission of large amounts of digital data, with very low power consumption. This technology is not influenced by the line-of-sight, or LOS, like the regular wireless connections, so objects that once blocked the digital data traffic, like in the Bluetooth technology, will now be almost ignored. The Bluetooth requires a pairing process, it is not very secure and the speed provided is pretty low. The WUSB is a major step forward compared with the Bluetooth. With this technology, at three meters, the transfer speed can go to 480Mbps and at ten meters, to even 110Mbps.
With the speed and security of wired technology, the wireless USB, or the WUSB, is the new trend of wireless devices. Just as Wi-Fi is replacing the Ethernet cable, the wireless USB will most likely replace the regular, wired USB technology. Very soon, devices like hard drives, flash drives, game controllers, digital cameras, printers, scanners, MP3 players or mobile phones will have integrated WUSB technology. Announced in May 2005, the wireless USB, using the Ultra Wide Band, or UWB, a wide spectrum frequency band that operates in the 3.1 to 10.6 GHz and allows the transmission of large amounts of digital data, with very low power consumption. This technology is not influenced by the line-of-sight, or LOS, like the regular wireless connections, so objects that once blocked the digital data traffic, like in the Bluetooth technology, will now be almost ignored. The Bluetooth requires a pairing process, it is not very secure and the speed provided is pretty low. The WUSB is a major step forward compared with the Bluetooth. With this technology, at three meters, the transfer speed can go to 480Mbps and at ten meters, to even 110Mbps.
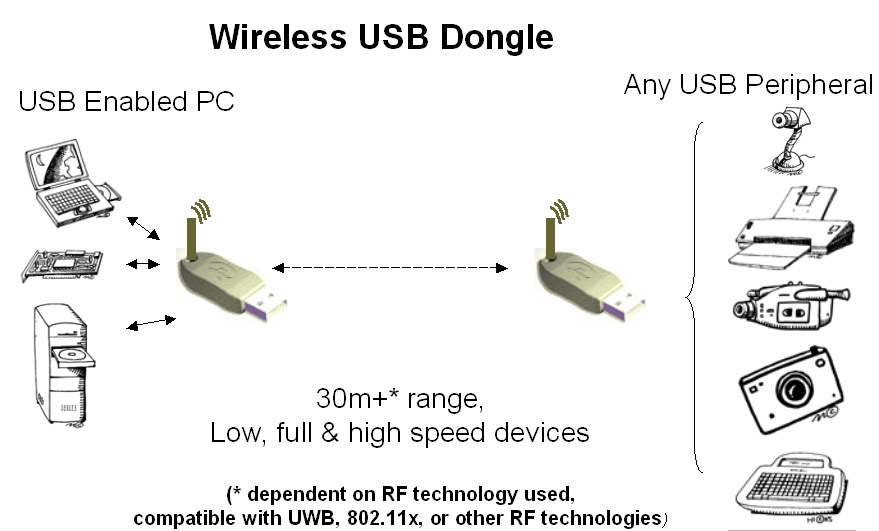
A combination of a PC connected USB antenna and a wireless USB hub with four regular wired USB ports, was designed by Belkin. This way, a computer can access, by sending and receiving, digital data from the USB devices connected to the wireless USB hub. Lenovo is one of the producers that already announced a laptop using built-in features of the wireless USB technology and I’m sure that many will follow very soon.
The WUSB technology is not new
In February 2004, the Wireless Promoter Group was founded, formed from NEC Corporation, Philips, Agere Systems, Samsung, Intel, Staccato Communications, Hewlett – Packard, Microsoft, Alereon and Wisair. This conglomerate of companies defined what we call today the Wireless USB protocol. As I previously stated, in May 2005, they announced the first version of the wireless USB and in June 2006, initial tests models were produced. After the US Federal Communications Commission tested the devices, in October 2006, the first retail product was released by IOGear, in the mid-2007, using components produced by Alereon, Intel and NEC.
The wireless USB design
The wireless USB design provides the connection to a host to large number of devices, 127 maximum, and it also supports dual-role devices. These devices that can act as a slave device when connected to a computer or as a limited ability host when connected to another device, all depending on how they are used. For example, a printer is normally a slave device and so is a digital camera when you connect them to your PC. But when you connect the digital camera to the printer, the camera will become a limited ability host.
Most likely, more wireless USB device will make their way in the IT market, devices for the end – users, as this technology makes the customers even more mobile and in the same time, it allows us to get rid of those annoying cables.